Grey’s AI-natomy: The Future of Medicine
Machine learning algorithms and artificial intelligence officially made it into medical jargon when the UK’s Exscientia announced the first drug discovered using AI became a candidate to go under human clinical trials. And yet, the World Health Organization has recently issued a statement calling for the safe and ethical use of AI in healthcare. So, which one is it? Can AI help medical professionals and improve patient outcomes? Or is the technology so new, and so unregulated, that it can’t be trusted with medical records?
Understanding AI in the Healthcare Industry
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning have made headlines with the promise of revolutionizing the healthcare industry. In the medical domain, AI encompasses both narrow and general AI, where narrow AI focuses on specific tasks while general AI aims for human-level intelligence.
Machine learning, deep learning, and natural language processing are key AI and large language model technologies that hold immense promise in healthcare, enabling advanced data analysis, predictive modeling, and efficient communication with patients. Data collection, analysis, and algorithm training are critical in empowering AI-driven healthcare solutions, enabling personalized diagnostics, enhanced treatment planning, and remote monitoring.
Remarkable examples of AI’s success include improved medical imaging analysis, drug discovery, and personalized medicine, demonstrating the tremendous power of AI in revolutionizing healthcare, all of which we discuss below.
Training and Limitations of Artificial Intelligence in the Medical Field
Artificial intelligence that is to be used in the medical field undergoes rigorous training to enhance its capabilities. Generative AI is trained using large datasets to learn patterns and generate human-like responses, enabling natural-sounding and interactive conversations.
However, AI models for medical use have limitations. The ones based on ChatGPT rely on data available up to 2021 because that is when the model stopped training. The need for extensive and diverse datasets is crucial to ensure accurate and reliable predictions. Always make sure to be informed about the limitations of the model before blindly trusting it.
Concerns about the reliability and accuracy of AI predictions and medical diagnoses exist precisely because of data limitations and bias, emphasizing the importance of human oversight and validation in the medical decision-making process.
Getting Accurate and Relevant Responses
Apart from the relevancy and amount of data the model was trained on, the accuracy and relevance of the AI’s response will lie in the way you phrase your request (prompt engineering). Prompt engineering allows healthcare professionals to craft specific and clear prompts, defining objectives and providing sufficient context to AI systems. This enhances the precision and clarity of responses received by healthcare institutions.
Furthermore, understanding hallucinations, a phenomenon where the AI confidently gives false facts as responses is crucial. This is why you must fact-check and engage in critical thinking when using tools like this, and not over-rely on them. To understand more about hallucinations (and other AI terms like neural networks, deep learning algorithms, and generative AI), check out our article about foundation models.
Applications for Medical Professionals and Medical Research
AI-powered technology is so rapidly evolving, that it can prove challenging to list the applications, and not have them already expanded by the time you are reading this. Below we included the current applications of artificial intelligence technology in medical diagnosis, medical devices, and the healthcare sector.
Enhancing Diagnostics and Medical Imaging
AI algorithms can be trained to differentiate between healthy and diseased patterns, enabling early detection of diseases like cancer and chronic diseases, and providing risk assessments.
Medical imaging is also being transformed by artificial intelligence techniques that analyze body scans to detect subtle differences undetectable to the human eye. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved about 420 algorithms for various diseases, helping healthcare providers detect conditions early and provide faster answers for patients.
Artificial intelligence is also improving patient monitoring by tracking even minor changes in conditions, particularly in cancer patients. Functional imaging techniques are being developed to assess tumor response to treatment and identify early signs of metastasis.
Some of the AI tools that already use this technology in medical diagnostics are:
- Enlitic: Healthcare data solutions provider that standardizes and analyzes data to improve clinical workflows and data management in healthcare.
- PathAI: AI-powered pathology solutions for accurate diagnoses and effective treatments through the management and analysis of whole slide images.
- Arterys: Precision medicine platform that enhances diagnostic decision-making and efficiency by extracting insights from medical images.
This technology holds immense benefits in improving diagnostic accuracy, reducing human error, and expediting patient care.
Personalized Medicine and Treatment Planning
Artificial intelligence can rapidly collect and synthesize relevant medical data together, providing personalized patient care planning. It can be used in various stages of the treatment process, such as risk assessment, diagnosis, disease management, and patient prognosis.
Real-world practical examples include increased cancer screening for patients with specific gene mutations and the use of human genetics in drug research. Several companies that have already implemented this kind of technology into their software are the following:
- Enlitic: Harnesses AI to transform clinical workflows and improve data management, specifically targeting personalized medicine and treatment planning.
- Linus Health: Next-generation digital cognitive assessment platform that enables early detection and intervention in brain health, focusing on Alzheimer’s and other dementias.
- Caption Health: Integrates AI with ultrasound technology to provide convenient and cost-effective echocardiograms, supporting personalized care pathways.
Despite funding and reimbursement challenges, the demand for preventive medicine is growing, and precision medicine holds promise in accelerating drug discovery, enhancing disease screening, and reducing overall healthcare costs.
Drug Discovery and Development
AI and deep learning accelerate the drug discovery and development process by leveraging its algorithms to analyze vast amounts of biomedical data and identify potential drug candidates. It offers tremendous potential in predicting drug properties, optimizing formulations, and reducing research costs. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recognizes the increasing use of AI and machine learning in drug development, with over 100 submissions reported in 2021 alone. Artificial intelligence and machine learning are integrated into various stages, from drug discovery to clinical research and postmarket safety surveillance, through scanning medical literature, predicting treatment responses, and developing digital patient models.
By training on large datasets and utilizing techniques like natural language processing and artificial neural networks, artificial intelligence can understand the biological mechanisms of diseases and identify novel proteins and genes as targets for drug development. AI systems like AlphaFold can even predict the 3D structures of targets, expediting the design of drugs that effectively bind to them.
Artificial intelligence is transforming various stages of drug discovery, including molecular simulations, prediction of drug properties, de novo drug design, candidate drug prioritization, and synthesis pathway generation. Several companies had success in implementing artificial intelligence into their process of drug discovery and drug development:
- Enlitic: Utilizes AI to address challenges in radiology and improve drug discovery and development processes.
- Arterys: Combines AI technology with human expertise to enhance diagnostic decision-making and productivity in drug discovery and development.
Advancements like these reduce the need for physical testing, accurately predict drug properties, optimize formulations, and enhance efficiency, thereby reducing research costs and improving patient care.
AI-Enabled Remote Monitoring and Telemedicine

AI-enabled remote patient monitoring and telemedicine have emerged as crucial tools in healthcare, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic. These technologies have facilitated the delivery of essential care to at-risk individuals in their homes, reducing the spread of the virus and enabling providers to offer comprehensive care for patients with acute and chronic illnesses.
By incorporating remote patient monitoring (RPM) into a patient’s care plan, clinicians can monitor vital signs and health data between visits, allowing for early intervention and timely adjustments to treatment.
Some of the software that have already been integrated with artificial intelligence in order to enhance remote patient monitoring are the following:
- Merative: Offers a connected healthcare ecosystem with clinical decision support, remote monitoring, and telemedicine capabilities.
- Viz.ai: Bridges the gap between patients, clinicians, and life-saving treatments through AI-powered care coordination and real-time patient information updates.
- Twill: Simplifies healthcare through digital-first care, personalized interventions, and telebehavioral health to connect individuals with the care they need.
- Buoy Health: AI-powered symptom checker and healthcare resource that helps users understand their health issues and find appropriate care.
- Caption Health: Integrates artificial intelligence with ultrasound technology for early disease detection and personalized care pathways, even in patients’ homes.
The integration of artificial intelligence further enhances the potential of RPM by improving patient adherence, boosting clinical efficiency, and fostering better patient outcomes.
Patient Care, Communication, and Support

Artificial intelligence can play a crucial role in providing initial responses to client inquiries and common medical questions, enhancing the patient care experience, especially in understaffed offices and hospitals. Artificial intelligence can assist staff in the healthcare industry in scheduling appointments, answering insurance questions, and providing follow-up on referrals.
Here is an example of ChatGPT crafting an email response to a client inquiry about available appointments:
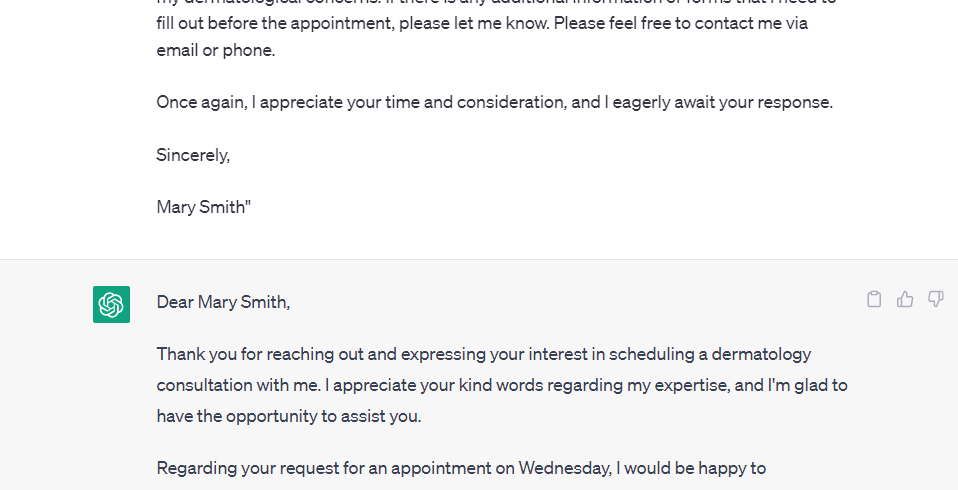
Machine learning technology can, especially when fine-tuned and given enough context, act as the doctor’s personal assistant or a secretary, and immensely help healthcare professionals and healthcare organizations save time and focus on patient care (and they can use one of the best AI time management tools to divide the extra time). Here are some of the current examples of AI assisting in just that:
- Viz.ai: Enhances care coordination, alerts, image viewing, and communication capabilities to transform patient care.
- Regard: Streamlines clinical, CDI, and revenue cycle efforts to improve hospital finances, patient safety, and physician satisfaction.
- Buoy Health: Simplifies healthcare navigation by providing reliable guidance and information on symptoms, self-care, and seeking urgent care.
- VirtuSense: Provides an AI-assisted fall prevention solution to enhance patient care and safety in various healthcare settings.
This kind of software can be a great budget choice for rural or understaffed healthcare organizations.
Unlocking AI’s Full Potential
There are a few ways to get the most out of any artificial intelligence that you may be using in the healthcare industry:
Customization and Training
By exposing the model to medical-specific data, it can develop a deeper understanding of medical terminology, conditions, and treatment options, leading to more accurate predictions and recommendations. However, it is crucial to approach customization with ethical considerations and caution. All of this data and electronic medical records need to come from real-life examples and people.

Ensuring the privacy and confidentiality of patient data and medical records, maintaining unbiased decision-making, and addressing potential biases or limitations in the dataset are paramount. Striking a balance between customization and preserving ethical standards is essential for harnessing the full potential of machine learning and AI in healthcare.
Crafting the Perfect Prompt
By carefully crafting their requests and questions (prompts), healthcare professionals and researchers can optimize the performance of AI systems, making sure that the generated responses align with the specific requirements and objectives of the medical domain. This tailored approach enables better diagnostics, treatment planning, drug discovery, and patient care. However, it is important to remain cautious of potential limitations and biases in AI-generated responses, requiring ongoing refinement and evaluation.
In order to craft the perfect prompt you should make sure to:
- Define the Objectives: Clearly state your objectives and the desired response to ensure the artificial intelligence understands your specific needs and goals.
- Craft Clear and Specific Prompts: Avoid ambiguity by providing precise instructions on what you want the AI to deliver.
- Provide Sufficient Context: Attach relevant documents, articles, or emails to help the artificial intelligence understand the specific circumstances and background information.
- Test and Refine Iteratively: Experiment with different prompts, refining them based on the AI’s responses to improve accuracy and relevance over time.
Here are a few examples of how to do exactly that: Let’s say you are looking into the efficiency of a certain drug (X) in treating patients over the age of 65 with a condition Y. You’d start with a prompt: “Can you provide information about the benefits of drug X for patients with condition Y?” The model will deliver a vague answer, not specific to your case.
Refinement 1: “Based on published research articles and real-world data, evaluate the effectiveness of drug X compared to standard treatments for patients with condition Y.” The model will review the data (keep in mind that in the case of ChatGPT, the data is only relevant up to 2021) and evaluate the effectiveness on all patients, not your specific case of over 65-year-olds.
Refinement 2 (with context): “Review the medical literature on drug X’s efficacy in treating patients with condition Y, focusing on studies involving patients over the age of 65 and considering any potential drug interactions with common medications in this population. [If needed, insert most relevant research]” The model will deliver your desired response.
Integration with Medical Tools and Platforms
During the pandemic, there was a spike in usage of digital healthcare platforms. Integrating artificial intelligence into the tools and software that are already in use could bring the platforms to the next level. Artificial intelligence integration holds significant potential for the healthcare industry, particularly in e-prescription systems, Hospital Management Systems (HMS), and Healthcare Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software.
In e-prescription systems, artificial intelligence algorithms can analyze patient data and medical histories to provide real-time recommendations, ensuring safer prescribing practices and reducing errors. For HMS, AI-powered analytics can optimize resource allocation, bed management, and surgery scheduling by processing large datasets. Additionally, chatbot integration in HMS can enhance patient engagement and provide automated support. In CRM software, AI algorithms personalize communication, automate appointment scheduling, and analyze patient feedback to improve services and satisfaction.
Another example is add-ons to existing document creation software, like Microsoft Word. Ghostwriter Medical is a ChatGPT-based extension that helps with medical document creation. Ghostwriter is just one example among many, but we took the time to review the best AI writing tools on the market.
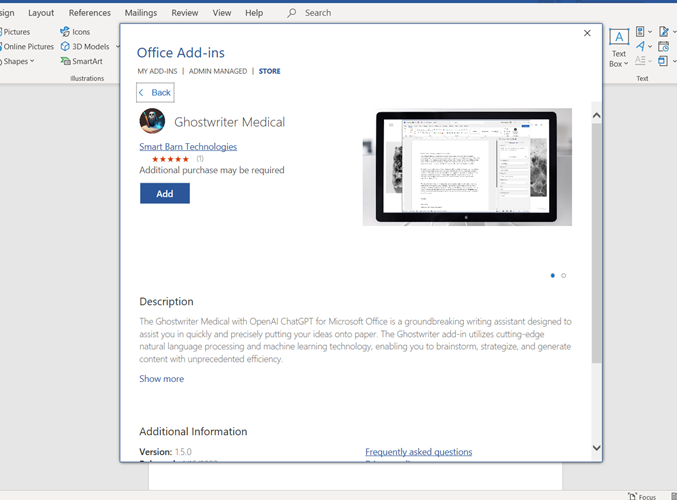
These integrations empower healthcare organizations to deliver efficient, personalized care, improve operational efficiency, and enhance patient experiences. AI’s potential in these areas reinforces its role in transforming and advancing the healthcare industry.
Ethical Considerations and Challenges
Since the world has only recently been introduced to artificial intelligence, rules, and regulations have still not been implemented in most cases. Yet, many ethical concerns arise, especially regarding data storage and privacy.
Ethical Considerations in the AI-Driven Healthcare
The integration of artificial intelligence into medical practice brings forth a range of ethical concerns that require careful consideration. Patient privacy and data security are paramount in the age of AI, as the use of computer science on sensitive health information raises concerns about unauthorized access and potential breaches. Before inputting the patient’s medical history (in the form of electronic medical records) into machine-learning models, the healthcare provider and the patient need to be informed about the storage of this information, and potential risk factors.
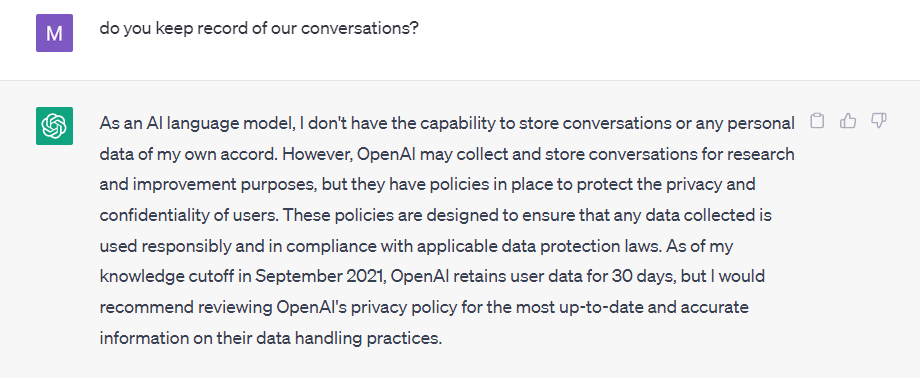
Moreover, machine learning algorithm bias poses a significant ethical challenge, as biased algorithms can result in unequal treatment and disparities in healthcare outcomes. To address these concerns, transparent and accountable AI systems are essential as well as the presence of human intelligence. The medical community is pushing for ethical guidelines and regulations to be established in order to govern the use of AI in medicine, promoting responsible practices and ensuring patient welfare.
Legal and Regulatory Challenges
Liability and malpractice are significant concerns when it comes to AI-driven healthcare, as errors or incorrect medical diagnoses made by AI systems can have serious consequences. In addition, existing medical device regulations may not fully account for the complexities of AI systems, necessitating the development of new regulatory frameworks. To ensure patient safety and responsible artificial intelligence use, robust governance frameworks and policies are required.
A step in the right direction when it comes to understanding what sort of regulations need to be imposed is the fact that Congress recently acquired and distributed 40 ChatGPT licenses. The policymakers will use the services for summarizing documents and experimenting with the possibilities and limitations of the models.
Ensuring Bias-Free and Fair AI in Medicine
Biased artificial intelligence predictions and diagnoses can lead to disparities in treatment and healthcare outcomes for different populations, perpetuating inequalities in healthcare. To mitigate these risks, diverse and representative datasets are necessary for training AI models.
Ongoing research and initiatives focus on developing unbiased AI systems in medicine, emphasizing the importance of algorithmic fairness and reducing bias in decision-making processes. By working towards bias-free and fair AI for medical professions, the healthcare industry can strive for equitable and accessible healthcare for all.
Patient Trust and Transparency

Building patient trust in AI-driven healthcare solutions is vital for successful implementation. Transparent communication and informed consent play a pivotal role in establishing trust. Patients should be well-informed about the use of AI in their healthcare, its potential benefits, and any associated risks.
Future efforts to enhance transparency need to include providing clear explanations of AI algorithms and ensuring that patients have the opportunity to participate in decision-making processes. By prioritizing patient trust and maintaining transparency, AI-driven healthcare can foster strong patient-provider relationships and enhance the overall quality of care.
The Future of the Healthcare Industry
With the rise of technologies such as robotics, precision medicine, and personalized AI assistants, the healthcare industry can become more efficient and tailored to individual needs. AI has the ability to make predictions, help with staffing and triage in emergency departments, as well as determining effective treatments for specific patient groups like women with breast cancer.
Natural language processing can aid in interpreting patient scans and identifying secondary issues for follow-up. Ongoing research, collaboration, and interdisciplinary efforts are vital for harnessing the full potential of AI in the healthcare industry.
Introducing artificial intelligence in the healthcare industry is still in the early stages. Generative AI in healthcare is still used mostly in research since the models we have available today cannot use medical devices, provide patient visits and administer medical care. While AI will augment the work of medical professionals, their expertise, empathy, and creativity will remain essential components of patient care, ensuring a win-win scenario for all involved.
Final thoughts
The integration of AI into the healthcare industry holds immense promise for diagnosing patients, improving patient outcomes, and treating chronic diseases. With the before-mentioned applications in diagnostics, medical imaging, personalized medicine, drug discovery, remote monitoring, and patient care, AI is transforming the way healthcare professionals operate.
However, the limited use of AI has already raised massive concerns regarding patient privacy and the assurance of drug safety and efficacy. As AI-enabled drug discovery and AI-assisted medical and patient care continue to evolve, it is essential for the healthcare industry as a whole and policymakers to work together to address these challenges in order to fully capitalize on the opportunities offered by AI and machine learning models. Working side by side, human and artificial intelligence could actually save the world, one patient at a time.